Neuroinfectious disease is a high-yield topic for all neurology exams. You should be familiar with the commonly tested viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections; especially how to diagnose and treat them. Here you will find the topics and facts with the most weight for RITE® and board exams, along with quality radiology and pathology images, flashcards, and a practice quiz!
Authors: Steven Gangloff MD, Brian Hanrahan MD
Congenital
Congenital rubella
- A neuroinfectious disease that causes cataracts, congenital heart defects (PDA), deafness, microcephaly, and developmental delay. Less likely hepatosplenomegaly and jaundice.
- MRI with periventricular and cortical (especially basal ganglia) calcifications.
Congenital Toxoplasmosis
- Causes chorioretinitis (usually bilateral), macrocephaly (due to intrauterine hydrocephalus), seizures, developmental delay, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, and purpuric rash.
- MRI with calcifications of the basal ganglia and corticomedullary junction.
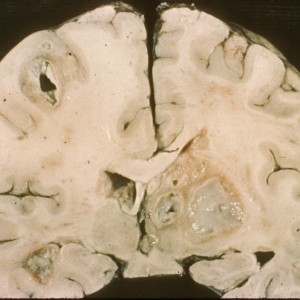
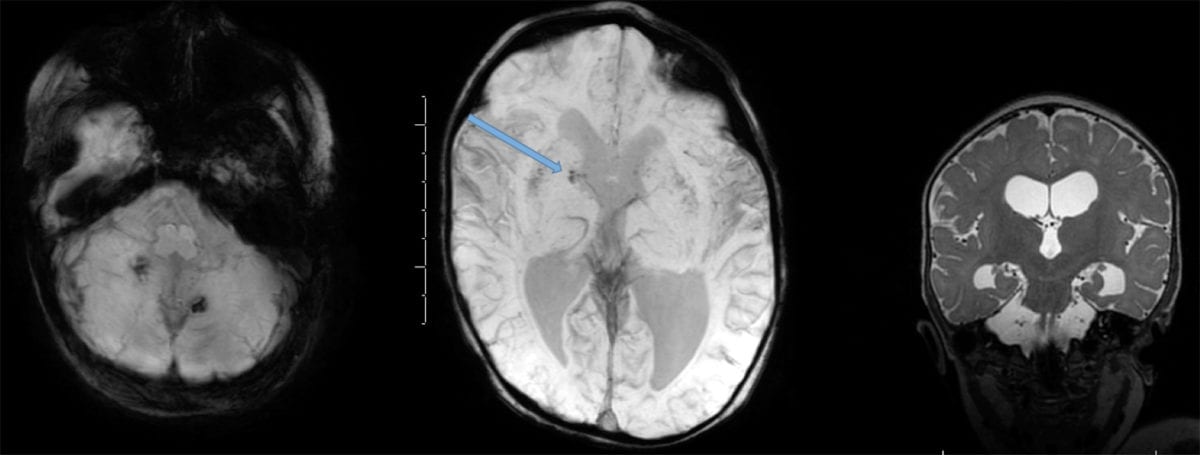
Congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Causes developmental delay, seizures, sensorineural deafness, hepatosplenomegaly, vision loss, microcephaly, and lissencephaly.
- This neuroinfectious disease is the leading cause of acquired hearing loss in childhood, and hearing loss may even occur in children who had an asymptomatic CMV infection at birth.
- Neuroimaging will show periventricular calcifications, profound cortical atrophy and ventriculomegaly. May also have associated anterior temporal cysts with white matter disease.
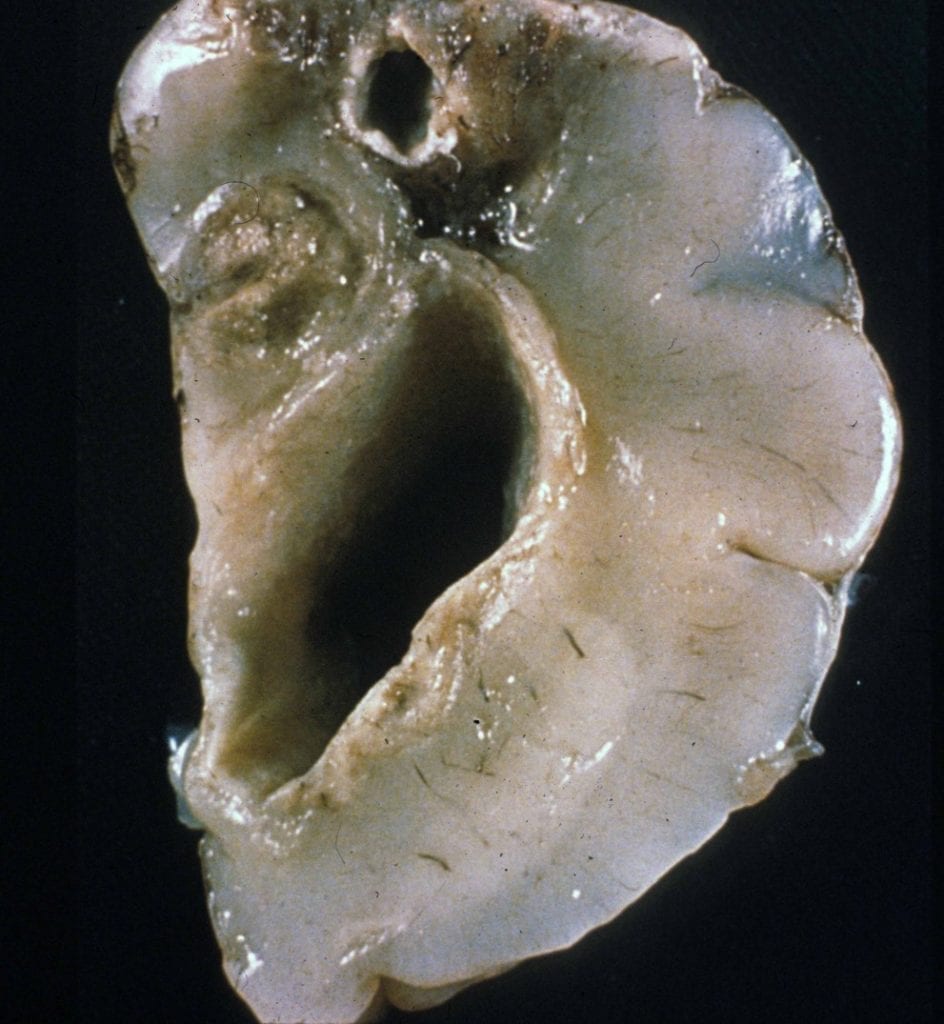
Neonatal herpes simplex
- Exposure to genital herpes through the birth canal.
- MRI with multifocal lesions, temporal lobe involvement, hemorrhages, and relative sparing of basal ganglia.
Congenital syphilis
- Presents at birth with mucoid or bloody nasal discharge (“snuffles”), long bone deformities, Hutchinson’s teeth, keratitis/blindness, and frontal bossing.
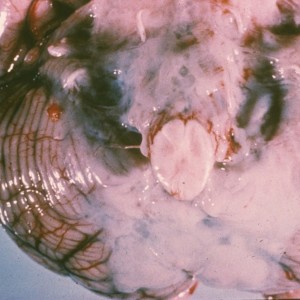
Congenital HIV/AIDS
- Symptom onset between 2 months and 5 years with a loss of milestones, failure of brain growth, ataxia, myoclonus +/- seizures, and spastic paresis.
- Pathology with multinucleated giant cells and calcific vasculopathy (see below).
- MRI with diffuse atrophy.
Bacterial
Bacterial Meningitis/Meningoencephalitis/Abscess
Causes of Bacterial Meningitis and Appropriate Treatments:
| Age Group | Most Common Pathogen | Antibiotics |
| Newborns <1 m.o. |
|
Cefotaxime and ampicillin (Must avoid ceftriaxone if less than 1 m.o. due to jaundice risk) |
| Children |
|
Ceftriaxone, vancomycin, acyclovir Plus dexamethasone if S. pneumoniae expected |
| Adolescents & Adults |
|
Ceftriaxone, vancomycin, acyclovir Plus dexamethasone if S. pneumoniae expected |
| Adults > 50 y.o. |
|
Ceftriaxone, vancomycin, acyclovir, ampicillin |
High Yield:
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common long-term complication of bacterial meningitis.
CNS abscess
- It is high yield to be able to identify CNS abscess on MRI:
- An abscess will have internal restricted diffusion due to the presence of pus, with a smooth rim of enhancement and adjacent vasogenic edema.
- If multiple lesions are present, consider septic emboli.
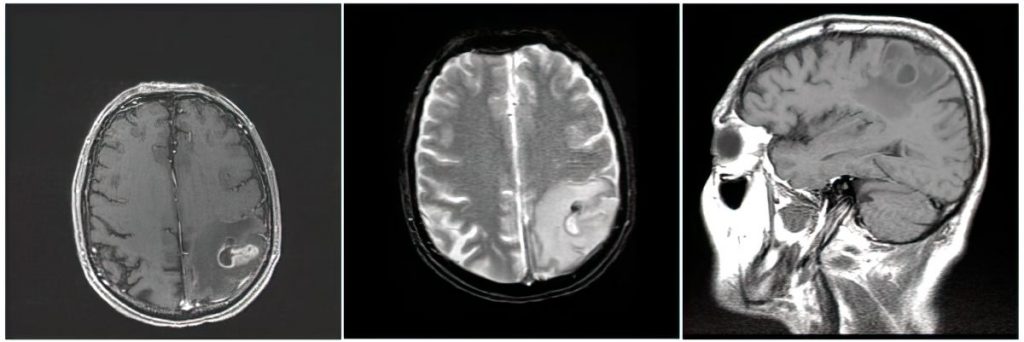
- Citrobacter species, Serratia marcescens, Proteus, Pseudomonas, and Enterobacter are common causes.
- Ventriculitis is another possible complication of meningitis:
- On MRI, ventriculitis appears as fluid levels within the cortical sulci and within the posterior horns of the lateral ventricles with increased signal and on the T1-weighted postcontrast views with extensive enhancement of the ependyma.
- Lasting sequela of bacterial meningitis can include hearing loss, permanent motor deficits, learning disability, epilepsy, and/or hydrocephalus.
- The most common cause of brain abscess in immunocompetent patients is spread from nearby infection (otitis, mastoiditis > sinusitis).
- This accounts for 40-50% of cases.
- Hematogenous spread (such as from endocarditis) accounts for 30-40% of cases.
- Spread from distal infection (such as dental) is possible, but less common.
- Most significant predisposing factor for bacterial abscess in children is cyanotic congenital heart disease.
- Treatment:
- Empiric brain abscess antibiotic treatment includes a third-generation cephalosporin and metronidazole.
- Because >95% of brain abscesses are bacterial, and of those many are polymicrobial, broad-spectrum coverage is needed until a brain aspiration can confirm the pathogen.
- An exception is if endocarditis is already confirmed or highly suspicious, in which case IV nafcillin is often used.
- In addition to antibiotics, surgical drainage is a needed treatment.
- Glucocorticoids can be considered if the abscess has mass effect large enough to cause significant depression of mental status.
- Empiric brain abscess antibiotic treatment includes a third-generation cephalosporin and metronidazole.
Log in to View the Remaining 60-90% of Page Content!
New here? Get started!
(Or, click here to learn about our institution/group pricing)1 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$142.49
$
94
99
1 Month -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
3 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$224.98
$
144
97
3 Months -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
1 Year Plan
Full Access Subscription
$538.47
$
338
98
1 Year -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
Popular
Loading table of contents...
Loading table of contents...