Neuromuscular junction diseases, particularly myasthenia gravis, are high-yield for neurology examinations because they command a deep understanding of pathology, diagnostic testing, and therapeutics. Test your knowledge with questions after completing this chapter packed with high-yield facts.
Author: Brian Hanrahan MD
Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
- MG is a postsynaptic autoimmune disease with antibodies directed toward acetylcholine receptors or receptor-associated proteins.
- Patients usually present with weakness, diplopia, dysarthria, and/or dysphagia. Symptoms worsen with sustained or repetitive activity and improve with rest.
- 15% of patients have only ocular deficits referred to as ocular myasthenia gravis.
- Associated with CTLA4 gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or exposure to ipilimumab.
Diagnostic tests
- Clinical testing
- The ice pack test (placing a bag of ice on a closed lid for two minutes) can be performed to look for improved ptosis as colder temperatures mediate neuromuscular transmission.
- The Tensilon (edrophonium) test can also be done but is rarely performed anymore in clinical practice.
- EMG testing:
- Single fiber electromyography is the most sensitive test for MG (but not specific). If pathologic it will show variable depolarization of a single action potential described as “jitter”.
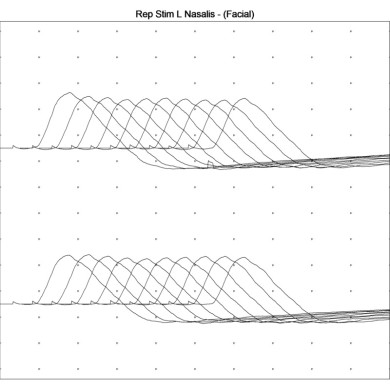
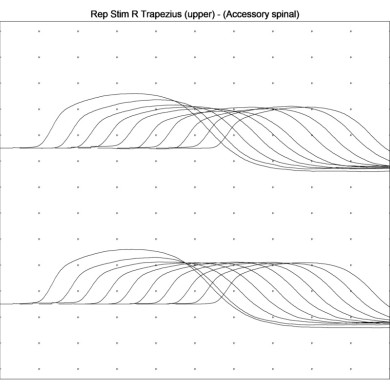
- Repetitive nerve stimulation at 2 to 3 Hz would show a decrement in compound muscle action potentials (CMAPs) due to the progressive failure of neuromuscular transmission.
- Antibody testing:
- ~85% of generalized MG cases and ~50% of ocular MG cases have anti-Acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibodies
Additional workup
- CXR vs. CT chest to evaluate for thymoma.
Medications to avoid with MG
- Quinolones, tetracyclines, antiarrhythmics, phenytoin, aminoglycosides, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, magnesium, lithium, and hydroxychloroquine.
Mnemonic: Please Be Most Concerned About QuALiTy: Phenytoin, Beta Blockers, Magnesium, Calcium channel blockers, Antiarrhythmics, Quinolones, Aminoglycosides, Lithium, Tetracyclines.
Treatment
- The anti-cholinesterase medication pyridostigmine (Mestinon) can produce immediate symptomatic improvement in muscle weakness but has no effect on the immunologic basis of the disorder.
- Can cause cholinergic side effects, including salivation, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- Prednisone is used as first-line therapy for patients with chronic disease but may transiently worsen weakness.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), intravenous methylprednisolone, and plasma exchange (PLEX) are used for acute exacerbations.
- Immunosuppressive agents like azathioprine and cyclosporine have a beneficial effect on weakness, but their benefit takes months to take effect.
- Eculizumab is a complement-binding monoclonal antibody approved for anti-Acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibody-positive MG
- Requires pretreatment meningococcal vaccine due to an Increased risk of meningococcal infection
- Thymectomy can lead to improvement of MG symptoms regardless if a thymoma is present or not!
Treatment in Pregnancy
- In approximately 40% of women, MG can worsen during pregnancy (typically during the first trimester).
- Acute exacerbation treatment should focus on IVIG. PLEX can be considered as second line. Steroids can be used in the second and third trimester, but may be associated with cleft palate if used in the first trimester.
- Methotrexate (Category X) and mycophenylate (Category D) are contraindicated due to teratogenicity.
- Pre-pregnancy thymectomy should be considered when possible.
Log in to View the Remaining 60-90% of Page Content!
New here? Get started!
(Or, click here to learn about our institution/group pricing)1 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$142.49
$
94
99
1 Month -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
3 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$224.98
$
144
97
3 Months -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
1 Year Plan
Full Access Subscription
$538.47
$
338
98
1 Year -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
Popular
Loading table of contents...
Loading table of contents...