The early days of endovascular thrombectomy for large vessel strokes were discouraging; the medical community didn’t know how to select the right patients for this type of procedure and techniques were not yet refined. In fact, in 2012 a large IMS III study showed that endovascular treatment offered no additional benefits. In the following year, two prominent papers published by the NEJM presented comparable findings.
However, in 2015 the MR CLEAN study showed that with the new clot retrieval systems and experienced practitioners, endovascular thrombectomy could improve functional outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke when compared to standard pharmacological therapy. Three years later, the DAWN trial proved that thrombectomy could benefit select patients up to 24 hours after they were last seen well. Patients who received thrombectomy were more likely to be functionally independent than those in the control group (49% vs. 13%, respectively). Additionally, there was no statistically significant difference in symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage or 90-day mortality.
From the pre-DAWN era to current times, endovascular thrombectomy has evolved from an unproven theory to part of the standard of care for ischemic strokes with large vessel occlusions in comprehensive stroke centers across the country. To put things into perspective, in 2012 only 3.3% of patients aged 80 or older with acute ischemic stroke had endovascular therapy in the United States. In 2019, that number jumped to 20.8%!
If you want a history lesson, reach out to your more veteran vascular neurology faculty to learn about the “pre-DAWN” times!
Read the Landmark Article here!
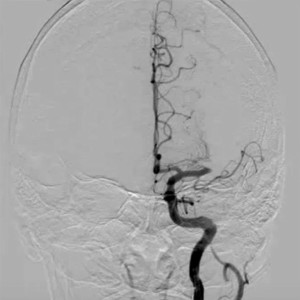
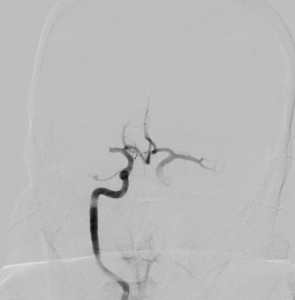
Check out these angiograms of large vessel occlusions from our image database:
References:
- Adcock AK, Schwamm LH, Smith EE, et al. Trends in Use, Outcomes, and Disparities in Endovascular Thrombectomy in US Patients With Stroke Aged 80 Years and Older Compared With Younger Patients. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(6):e2215869. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.15869
- Albers GW et al. A multicenter randomized controlled trial of endovascular therapy following imaging evaluation for ischemic stroke (DEFUSE 3). Int J Stroke 2017. 12:896-905.
- Berkhemer OA, Fransen PSS, Beumer D, et al. A Randomized Trial of Intraarterial Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke. 2014;372:11-20.
- Nogueira RG, et al. “Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct”. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2018. 378(1):11-21.
- Powers WJ, et al. American Heart Association Stroke Council. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018 Mar;49(3):e46-e110.